How do you test the breathability of a face mask?
To test the breathability of a face mask, there are several methods and standards that can be followed. I'll provide a concise explanation of the most commonly used approaches.
1. Differential Pressure Test:
The most common method to evaluate the breathability of a face mask is the differential pressure test. This test measures the airflow resistance of the mask material. It determines how easily air can pass through the mask, indicating its breathability. The test is conducted by measuring the pressure drop across the mask material while a constant airflow is applied. The lower the pressure drop, the easier it is to breathe through the mask. ASTM F2100 and EN 14683 are widely accepted standards for this test.
This test determines the permeability or airflow resistance of a face mask. It measures how easily air can pass through the mask material by using a specific airflow rate. The test apparatus consists of a chamber, a vacuum source, and a pressure gauge. The face mask is clamped between the two sides of the chamber, and the pressure difference is measured. This method is commonly used to evaluate the breathability of surgical masks.
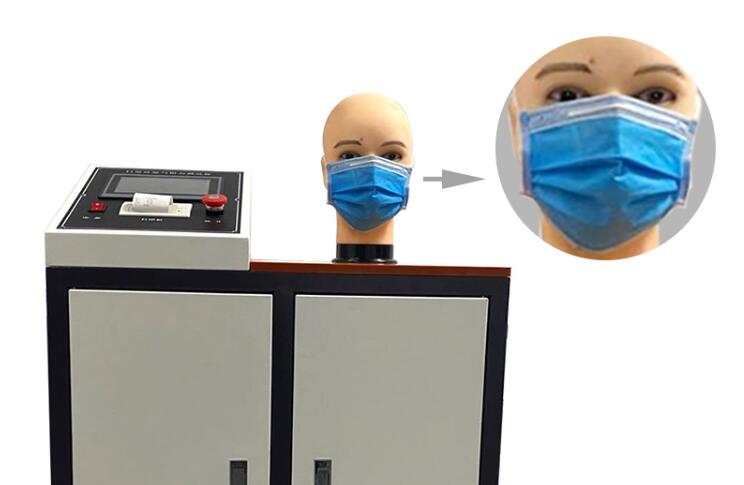
3. Water Vapor Transmission Rate (WVTR) Test:
WVTR test assesses the moisture vapor permeability of a face mask. The moisture vapor transmission rate is an indicator of how effectively the mask allows moisture (such as sweat) to escape from the wearer's face. To perform this test, the mask material is sealed over the mouth of a water-filled dish. Then it is placed in a controlled environment where the humidity is lower on one side and higher on the other. The weight loss of the water over time is recorded, indicating the amount of moisture that has transmitted through the mask.
4. Heat and Moisture Exchange (HME) Test:
An HME test evaluates the heat and moisture exchange properties of a face mask. It measures the ability of the mask to retain moisture and heat from exhaled breath while ensuring comfortable breathing. This test is often performed in conjunction with a breathing simulator that mimics human respiration. The face mask is placed on the breathing simulator, and the temperature and humidity changes of the inhaled and exhaled air are measured. The mask's performance is assessed based on its ability to maintain appropriate humidity and temperature levels.
5. Comfort Evaluation:
Apart from quantitative tests, subjective evaluations are also important in assessing breathability. Test subjects wear the face mask and provide feedback regarding ease of breathing, comfort, and any other discomfort experienced during use. This subjective evaluation can complement the objective test results and provide a holistic understanding of the mask's breathability.
It is worth noting that different countries and organizations may have specific standards or guidelines for evaluating face mask breathability. The methods mentioned above provide an overview of the common approaches used in the industry. Manufacturers and regulatory bodies should consult relevant standards and regulations to ensure compliance and safety.

