what is limiting oxygen index of polymers?
The Limiting Oxygen Index (LOI) is a measure of the flammability or combustibility of a polymer material, expressed as the minimum concentration of oxygen required for combustion to sustain itself in a test environment. It is an important parameter that helps assess the fire safety characteristics of polymers.
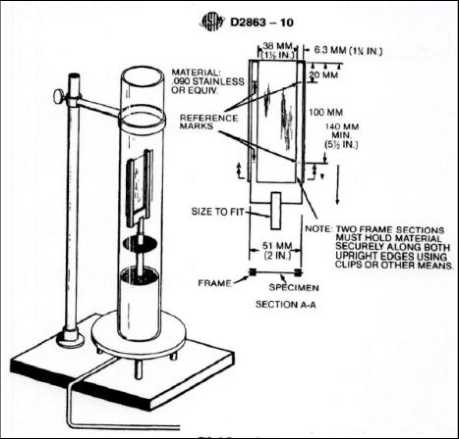
The LOI value is determined by subjecting a narrow strip or rod of the polymer to a controlled flow of oxygen and a controlled ignition source. The oxygen concentration is gradually reduced until the material stops burning. The LOI is then calculated as the percentage of oxygen (by volume) at which the combustion ceases.
A higher LOI value indicates that a polymer is less flammable, as it requires a higher concentration of oxygen to support combustion. Materials with a high LOI value are considered to have better fire-retardant properties.
The LOI value depends on several factors, including the chemical composition of the polymer, its molecular structure, and any additives or fillers present in the material. Polymers with dense molecular structures, high molecular weights, and a higher percentage of non-combustible components tend to have higher LOI values.
The LOI value provides valuable information for material selection in applications where fire safety is a concern. For example, construction materials used in buildings and transportation vehicles often require high LOI values to comply with fire safety regulations. By choosing polymers with high LOI values, the risk of fire and the spread of flames can be minimized.
In summary, the Limiting Oxygen Index (LOI) is a measure of a polymer's flammability, indicating the minimum concentration of oxygen required for combustion. It allows for the evaluation of a polymer's fire safety characteristics and is an important consideration in material selection for applications where fire safety is paramount.

