Oxygen Index Testing: Key Considerations and Best Practices
Oxygen Index (OI) testing is a critical procedure used to evaluate the flammability characteristics of materials. It measures the minimum concentration of oxygen in a mixture with nitrogen that will support the combustion of a material under specified test conditions. Here are some key considerations and best practices for Oxygen Index testing:
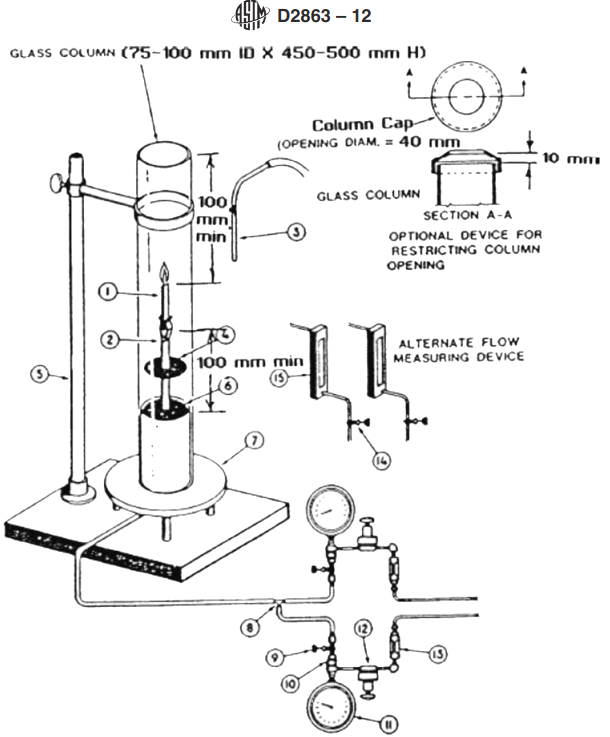
Key Considerations:
Sample Preparation:
- Ensure that the samples are prepared according to relevant standards or specifications.
- Samples should be representative of the material in its actual use, considering factors like thickness and density.
Sample Size and Shape:
- The dimensions of the sample can affect the test results. Follow the specified dimensions according to the relevant standard.
- Common sample shapes include rectangles or strips, and the thickness is often a critical factor.
Testing Standards:
- Choose the appropriate testing standard for your specific material. Common standards include ASTM D2863 and ISO 4589-2 for plastics.
- Familiarize yourself with the details and requirements of the chosen standard.
Testing Apparatus:
- Use a calibrated and well-maintained Oxygen Index apparatus.
- Ensure that the apparatus meets the requirements specified in the testing standard.
Oxygen and Nitrogen Purity:
- Use high-purity oxygen and nitrogen to achieve accurate and reliable results.
- Regularly check and maintain the gas sources to ensure their purity.
Ignition Source:
- The ignition source should be consistent with the testing standard.
- Common ignition sources include a gas burner or a nichrome wire.
Ignition Time and Observation:
- Record the ignition time accurately according to the testing standard.
- Carefully observe the burning characteristics, including flame spread and any dripping of molten material.
Test Environment:
- Conduct tests in a controlled environment with minimal air currents to avoid interference with the combustion process.
Data Recording:
- Record all relevant data, including sample dimensions, test conditions, and observations.
- Keep detailed records for traceability and future reference.
Calibration:
- Regularly calibrate the equipment according to the manufacturer's guidelines or testing standards.
- Calibration ensures the accuracy and reliability of the results.
Best Practices:
Training:
- Ensure that personnel involved in the testing are adequately trained on the equipment, procedures, and safety precautions.
Quality Control:
- Implement a quality control program to monitor and maintain the accuracy and precision of the testing process.
Safety Precautions:
- Follow safety protocols to protect personnel and equipment during testing.
- Have appropriate fire safety measures in place.
Documentation:
- Maintain comprehensive documentation for each test, including any deviations from standard procedures.
Data Analysis:
- Use appropriate statistical methods for data analysis to ensure the reliability of results.
Regular Maintenance:
- Regularly inspect and maintain the testing equipment to ensure it operates correctly.
Periodic Proficiency Testing:
- Participate in proficiency testing programs to validate the accuracy of your laboratory's results.
By adhering to these key considerations and best practices, you can enhance the reliability and repeatability of Oxygen Index testing and ensure the safety and quality of materials. Always refer to the specific testing standards relevant to your material and application for detailed guidance.

